Folate-containing reduction-sensitive lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin
Abstract
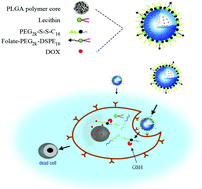
The development and evaluation of folate-targeted and reduction-triggered biodegradable nanoparticles are introduced to the research on targeted delivery of doxorubicin (DOX). This type of folate-targeted lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles (FLPNPs) is comprised of a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) core, a soybean lecithin monolayer, a monomethoxy-poly(ethylene glycol)-S-S-hexadecyl (mPEG-S-S-C16) reduction-sensitive shell, and a folic acid-targeted ligand. FLPNPs exhibited high size stability but fast disassembly in a simulated cancer cell reductive environment. The experiments on the release process in vitro revealed that as a reduction-sensitive drug delivery system, FLPNPs released DOX faster in the presence of 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT). Results from flow cytometry, confocal image and in vitro cytotoxicity assays revealed that FLPNPs further enhanced cell uptake and generated higher cytotoxicity against human epidermoid carcinoma in the oral cavity than non-targeted redox-sensitive and targeted redox-insensitive controls. Furthermore, in vivo animal experiments demonstrated that systemic administration of DOX-loaded FLPNPs remarkably reduced tumor growth. Experiments on biodistribution of DOX-loaded FLPNPs showed that an increasing amount of DOX accumulated in the tumor. Therefore, FLPNPs formulations have proved to be a stable, controllable and targeted anticancer drug delivery system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...