A reactive probe for Cu2+ based on the ESIPT mechanism and its application in live-cell imaging†
Abstract
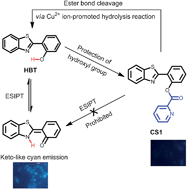
A new reactive probe based on an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) mechanism is reported for the selective detection of Cu2+ by the copper induced hydrolysis reaction. The probe is demonstrated to detect Cu2+ in living cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...