Bioanalytical and chemical sensors using living taste, olfactory, and neural cells and tissues: a short review
Abstract
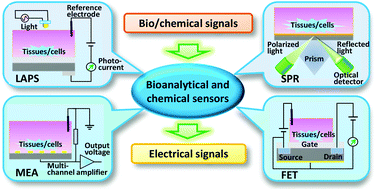
Biosensors utilizing living tissues and cells have recently gained significant attention as functional devices for chemical sensing and biochemical analysis. These devices integrate biological components (i.e. single cells, cell networks, tissues) with micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS)-based sensors and transducers. Various types of cells and tissues derived from natural and bioengineered sources have been used as recognition and sensing elements, which are generally characterized by high sensitivity and specificity. This review summarizes the state of the art in tissue- and cell-based biosensing platforms with an emphasis on those using taste, olfactory, and neural cells and tissues. Many of these devices employ unique integration strategies and sensing schemes based on sensitive transducers including microelectrode arrays (MEAs), field effect transistors (FETs), and light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPSs). Several groups have coupled these hybrid biosensors with microfluidics which offers added benefits of small sample volumes and enhanced automation. While this technology is currently limited to lab settings due to the limited stability of living biological components, further research to enhance their robustness will enable these devices to be employed in field and clinical settings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...