A novel substitution -sensing for hydroquinone and catechol based on a poly(3-aminophenylboronic acid)/MWCNTs modified electrode†
Abstract
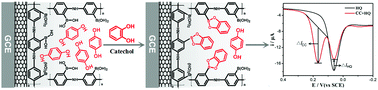
A facile electrochemical sensor for hydroquinone (HQ) and catechol (CC) determination was successfully fabricated by the modification of poly(3-aminophenylboronic acid) (pAPBA) film and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on a glassy carbon electrode (pAPBA/MWCNTs/GCE). The prepared sensor was characterized by scanning electron microscope and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Under optimal conditions, differential pulse voltammetry was employed to quantify individual HQ and CC within the concentration range of 5.0 × 10−7–4.0 × 10−5 mol L−1 and 7.0 × 10−6–1.0 × 10−4 mol L−1, respectively. Based on the covalent binding between the boronic acid groups of pAPBA film and the cis-diol-containing molecule, a novel substitution-sensing strategy was proposed for the highly sensitive determination of CC. With the addition of CC into HQ solution, covalent interaction between CC and APBA occurred and the HQ was displaced by CC, resulting in a decrease of HQ oxidation peak current and the increase of the CC oxidation peak current. The summation of both current changes (Δ|IHQ| + Δ|ICC|) were combined for CC sensitive detection in a concentration range of 4.0 × 10−8–1.7 × 10−5 mol L−1 with a limit of detection of 4.3 × 10−9 mol L−1. The sensor was successfully applied to the determination of CC in spiked water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...