Mesomorphism of a new series of catanionic 4-(1-pentylheptyl)benzenesulfonates†
Abstract
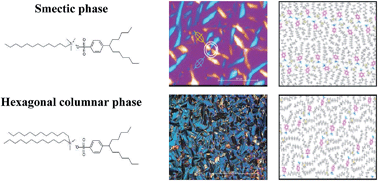
The effect of cationic chemical structure on the mesophase behavior, and self-assembly of catanionic compounds is studied through a systematic structure variation of six cationic surfactants with anionic sodium 4-(1-pentylheptyl)benzenesulfonate surfactant. A series of cationic surfactants are selected with an increasing number of n-dodecyl chains on the same ammonium headgroup (from one to three), and with an increasing number of ammonium headgroups (from two to four). Thermal and phase behavior of the synthesized products were examined by thermogravimetry, polarizing microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, powder and grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, and molecular simulation. The compounds are complexes of high thermal stability. Most of the thermotropic mesophases are smectic, although the hexagonal mesophase is also observed. Introduction of the third dodecyl chain into the cationic part leads to pronounced lower melting temperatures and eradicates mesomorphism, while the addition of a fourth ammonium headgroup leads to a catanionic benzenesulfonate that decomposes simultaneously under melting. Melting and crystallization temperatures show nonlinear dependence on the total number of alkyl chains, and on the number of headgroups in the molecule. Molecular dynamics simulation of the smectic phase points to separated hydrophilic and hydrophobic layers, favoring head-to-head packing of antiparallel molecules. On the other hand, there are two ion pairs in the column cross-section of the hexagonal LC phase of didodecyldimethylammonium-4-(1-pentylheptyl)benzenesulfonate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...