Lipidic spherulites as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents†
Abstract
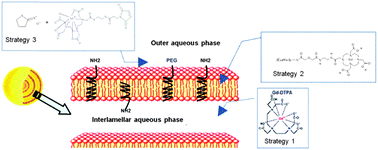
Magnetic resonance imaging is an excellent technique to achieve anatomical details and highly resolved images. The search for efficient contrast agents to increase the signal to background ratio led us to evaluate paramagnetic spherulites as potential Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) contrast agents. Spherulites are supramolecular assemblies, made of lipidic concentric multilayers, able to encapsulate with high efficiency soluble macromolecules. Despite their highly interesting structure, spherulites have never been proposed as imaging agents. We proposed here three approaches to render spherulites paramagnetic: encapsulating a soluble contrastophore, inserting a lipidic contrastophore derivative or grafting a soluble contrastophore at the surface of the spherulites. Following similar strategies, liposomes were prepared for comparison. The conservation of the spherulite structure, throughout these three strategies, was shown by cryoelectron microscopy and small angle light scattering. The effect of the paramagnetic spherulites was studied by magnetic resonance imaging at different magnetic fields. The results showed that insertion of a contrastophore lipidic derivative into spherulite bilayers and grafting a contrastophore at the surface of the spherulites were the two strategies which led to the highest MRI contrast improvement.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioinspired systems in supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...