Boosting the salt recognition abilities of l-ornithine based multitopic molecular receptors by harnessing a double cooperative effect†
Abstract
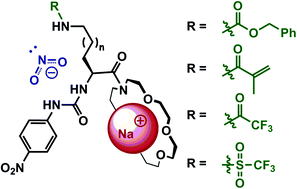
A family of L-ornithine based salt receptors 1a–f was synthesized, bearing a cation binding site and multiple anion binding sites (nitrophenylurea and amide groups) that may simultaneously associate with a single anion. The variation in H-bond donor abilities of one of these anion binding sites has relatively little influence on NO2− anion binding when the anion is accompanied by a noncoordinating TBA cation. However, in the presence of a sodium cation, which strongly coordinates with the cation binding domain of 1a–f, the increased H-bond donor abilities of the anion binding group result in a significant enhancement of NO2− anion binding. A direct correlation between the anion binding site H-bond donor tendencies and the binding cooperation of sodium cations and nitrite anions was also observed. Cation complexation fixes the nitrophenylurea moiety orientation and exposes that domain to bind anions. This cation and anion cooperation induces a second cooperative effect, namely the simultaneous association of a single anion with both urea and amide binding groups. Receptor 1d was found to be highly selective for NaNO2 over sodium bromide and nitrate. A transport experiment using a bulky liquid membrane showed that this receptor can effectively transport NaNO2 from the aqueous phase through the organic phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...