Alternating polymer micelle nanospheres for optical sensing†
Abstract
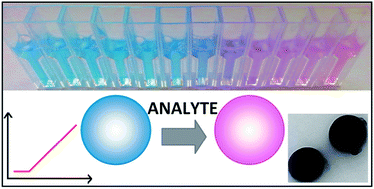
A novel concept of nanosized fluorimetric sensors is proposed, using alternating polymers as self assembling micelles that can be crosslinked resulting in stable polymeric nanoparticles. The thus obtained nanospheres have sizes close to 250 nm or 130 nm, depending on the preparation procedure and the negative surface charge, due to the presence of carboxyl groups on the surface. By a simple procedure, the nanospheres can be effectively loaded with compounds of choice, e.g. ionophores and ion-exchangers previously used to induce ionic sensitivity in polyacrylate or poly(vinyl chloride) micro- and nanospheres (miniature optrodes), thus allowing for optical or fluorimetric quantification of analytes. As a proof of concept, H+ sensitive colorimetric and fluorimetric sensors and K+ fluorimetric sensors using classical optrode approach were prepared and tested. The obtained sensors were characterized by high sensitivity, fast and reversible responses. Both K+ and H+ sensors were characterized by a broad response range resulting from the significant effect of processes occurring on the surface of the nanospheres. Due to this effect, the fluorimetric responses of the obtained spheres are significantly different from those typically observed for miniature optrode systems, and were linear within a range of at least 5 logarithmic units of analyte concentration. As shown, the surface groups of the herein proposed nanospheres can be used for the covalent linking of fluorophores that can be used as markers (if applied alone) or as reference dyes for fluorescent ion-sensitive nanospheres.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...