Nonlinear optical chromophores containing a novel pyrrole-based bridge: optimization of electro-optic activity and thermal stability by modifying the bridge†
Abstract
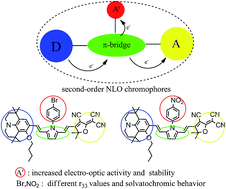
Three novel second order nonlinear optical chromophores based on julolidinyl donors and tricyanovinyldihydrofuran (TCF) acceptors linked together via modified pyrrole π-conjugation (chromophores A and B) or thiophene moieties (chromophore C) as the bridges have been synthesized and systematically characterized. In particular, the pyrrole moiety bridge has been modified with the electron withdrawing group (–Br, –NO2) substituted benzene ring. The introduction of side phenyl groups to chromophores A and B can increase the thermal and chemical stability and reduce dipole–dipole interactions so as to translate their hyperpolarizability (β) values into bulk EO performance more effectively than chromophore C. Moreover, DFT calculations suggested that the additional electron withdrawing groups in chromophores A and B could increase the β value compared to that of chromophore D without substituted phenyl groups, and they showed different influences on the solvatochromic behavior, thermal stability, and electro-optic activity of the chromophores. EO responses (r33 values) of guest–host polymers containing pyrrole-bridged chromophores were reported. Incorporation of chromophores A and B into APC provided large electro-optic coefficients of 86 and 128 pm V−1 at 1310 nm with a high loading of 30 wt%. Film-C/APC containing 25 wt% of chromophore C provides an EO coefficient of 98 pm V−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...