A novel protocol for generating high-affinity ssDNA aptamers by using alternating magnetic fields†
Abstract
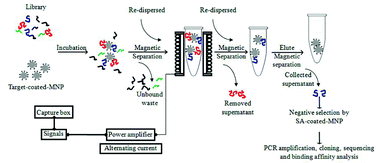
Background: Aptamers that have been generated using a SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment) process have been found to have high specificity and affinity with molecular targets, and, as a result, have found use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. The SELEX protocol generally requires 5 to 15 rounds of selection to generate high-affinity aptamers; however, the standard protocol is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Here, we propose a method for DNA aptamer screening, in which the evolutionary process is completely abandoned. Methods: The working principle of this new protocol, Magnetic-Assisted Rapid Aptamer Selection (MARAS), is discussed. We used C-reactive protein, a common cardiovascular disease (CVD) indicator, as a molecular target. An externally applied alternating magnetic field, aided by target-bound magnetic nanoparticles, was used to provide the competitive mechanism for the selection of DNA aptamers with different affinities to the target protein. Results: The range of the dissociation constants of the screened aptamers was approximately several nMs, depending on the frequency and the field strength of the externally applied alternating magnetic field. We also compared the diagnostic applicability of the aptamers generated by the proposed MARAS protocol with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), using antibodies. Conclusions: The proposed MARAS protocol efficiently generates aptamers that have high affinity and specificity with molecular targets. In addition, the proposed protocol represents significant time savings, as it can be completed in less than an hour. Furthermore, due to the simplicity of the MARAS protocol, we suggest that the proposed process could be easily automated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...