Magnetic Ni and Ni/Pt hollow nanospheres and their catalytic activities for hydrolysis of ammonia borane†
Abstract
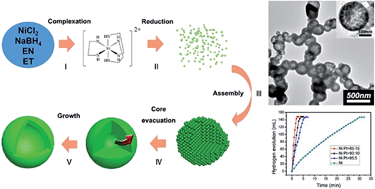
Hollow metallic nickel nanospheres have been controllably synthesized via a solvothermal reduction process. The complexation between ethylenediamine and Ni2+ might be the key factor to control the formation of the hollow structure through the reduction rate of Ni2+ at a relatively low level. The size of the hollow nanospheres could be adjusted by changing the starting ethanol/ethylenediamine volume ratio. The magnetic property study reveals that the coercivity of the as-synthesized hollow nickel nanospheres is much enhanced compared with that of bulk nickel materials. Ni/Pt hollow bimetallic nanospheres have also been synthesized by using the replacement reaction. Inspiringly, the as-synthesized Ni/Pt hollow bimetallic nanospheres exhibit higher catalytic activities for the hydrogen generation from ammonia borane hydrolysis compared with the Ni/Pt nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...