AgPd nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high performance catalysts for catalytic dehydrogenation of formic acid†
Abstract
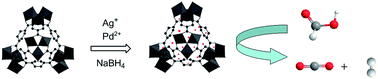
Bimetallic AgPd nanoparticles were successfully immobilized into the metal–organic frameworks (MIL-101), and tested for their catalytic dehydrogenation of formic acid. These catalysts were composition dependent for the catalytic activity. Among all the AgPd@MIL-101 catalysts tested, the Ag20Pd80@MIL-101 catalyst exhibits the highest catalytic activity for the conversion of formic acid to high-quality hydrogen at 80 °C with a TOF value of 848 h−1, which is among the highest values reported at 80 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...