Core–shell inversion by pH modulation in dynamic covalent micelles†
Abstract
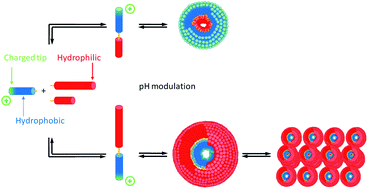
Dynamic covalent surfactants have been obtained by the reversible condensation of a hydrophobic aldehyde (ended by an ionic tip) with various neutral polyethylene glycol based hydrophilic amines. In water, the duality between the two hydrophilic domains (charged and neutral) leads to their segregation when the surfactants are self-assembled within micelles. Depending on the number of polyethylene glycol units, a core–shell inversion leading to a switching orientation of the ionic tips from the inside to the outside of the micelles has been demonstrated by a combination of scattering techniques. In competition experiments, when several amines of different pKas and hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chains are competing for the same aldehyde, it becomes possible to trigger this core–shell inversion by pH modulation and associated dynamic constitutional reorganization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...