A study of generation and rupture of soap films
Abstract
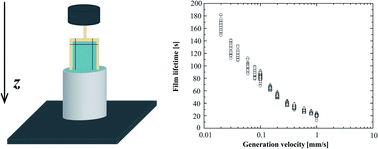
What are the lifetime and maximum length of a soap film pulled at a velocity V out of a bath of soapy solution? This is the question we explore in this article by performing systematic film rupture experiments. We show that the lifetime and maximal length of the films are fairly reproducible and controlled only by hydrodynamics. For surfactants with high surface elastic modulus, we argue that the rupture is triggered by the expansion of a thinning zone at the top of the film. The length  tz of this zone expands with time at a velocity equal to V/2, which can be obtained by a balance between gravity and viscous forces. The film lifetime is then found to decrease with the pulling velocity V, which implies that the surface tension gradient along the film increases with V. This surface tension gradient is found to be surprisingly small. Finally, the lifetime of films stabilised by solutions with small surface elastic modulus turns out to be much shorter than the ones for films with rigid interfaces.
tz of this zone expands with time at a velocity equal to V/2, which can be obtained by a balance between gravity and viscous forces. The film lifetime is then found to decrease with the pulling velocity V, which implies that the surface tension gradient along the film increases with V. This surface tension gradient is found to be surprisingly small. Finally, the lifetime of films stabilised by solutions with small surface elastic modulus turns out to be much shorter than the ones for films with rigid interfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...