Continuous-flow focusing of microparticles using induced-charge electroosmosis in a microfluidic device with 3D AgPDMS electrodes†
Abstract
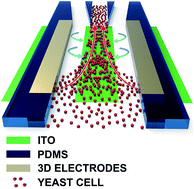
We herein present for the first time a microfluidic device that utilizes AC induced-charge electro-osmosis (ICEO) to continuously focus microparticles from suspending medium. An advanced conducting silver-polydimethylsiloxane (AgPDMS) composite is chosen to fabricate three dimensional (3D) driving electrodes thereby to generate a uniform AC electric field, resulting in a vortex ICEO flow on a planar floating electrode positioned at the bottom of the main channel. The 3D electrodes are employed due to their advantage of avoiding negative effects of alternating current electro-osmosis (ACEO) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). The combination of the ICEO flow and forward flow in the device channel focuses the microparticles in a thin stream and collects them in a specific outlet. We design the device based on the non-linear electrokinetic theory and flow field simulation, and validated the device performance under different experimental conditions including signal frequency, potential amplitude, and inlet flow rate. The highest focusing efficiency for yeast cells can reach 96.6% at the frequency of 600 Hz and a potential amplitude of 15 Vp. The results provide a promising method to flow-focus microparticles in modern microfluidic systems by using ICEO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...