Cooxidant-free TEMPO-mediated oxidation of highly crystalline nanocellulose in water†
Abstract
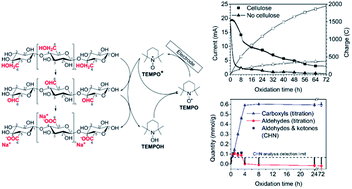
Selective oxidation of C6 hydroxyls to carboxyls through 2,2,6,6,-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-mediated oxidation, where the oxidizing species (TEMPO+) is generated by cooxidants, such as NaBrO, NaClO or NaClO2, has become a popular way to modify the surfaces of nanocellulose fibrils in aqueous solutions. Employing highly crystalline nanocellulose from Cladophora sp. algae we demonstrate that the same degree of oxidation (D.O.) can be achieved within approximately the same time by replacing the cooxidants with electrogeneration of TEMPO+ in a bulk electrolysis setup. The D.O. is controlled by the oxidation time and the maximum D.O. achieved (D.O. 9.8%, 0.60 mmol g−1 of carboxylic acids and 0 mmol g−1 aldehydes) corresponds to complete oxidation of the surface-confined C6. This shows that TEMPO+ is not sterically hindered from completely oxidizing the fibril surface of Cladophora nanocellulose, in contrast to earlier hypotheses that were based on results with wood-derived nanocellulose. The oxidation does not significantly affect the morphology, the specific surface area (>115 m2 g−1) or the pore characteristics of the water-insoluble fibrous particles that were obtained after drying, but depolymerization corresponding to ∼20% was observed. For extensive oxidation times, the product recovery of water-insoluble fibrils decreased significantly while significant amounts of charge passed through the system. This could indicate that the oxidation proceeds beyond the fibril surface, in contrast to the current view that TEMPO-mediated oxidation is confined only to the surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...