Chiral sensing for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy recognition of lysine enantiomers based on a nanostructured composite
Abstract
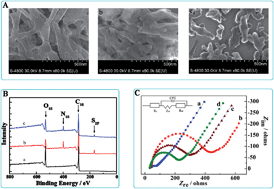
A simple and reliable chiral sensing platform for enantioselective recognition of lysine (Lys) enantiomers based on a nanostructured composite (NC) via the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique was described. The NC has been successfully synthesized through covalent linkage among the semiconductor 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid (PTCA), thionine (Thi) and chiral selector L-N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-O-benzylserine (L-BBSer). The stepwise synthesis process of the NC was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and EIS. The enantioselective interaction assay between NC modified glassy carbon electrode and lysine enantiomers relied on EIS technology. As a prototype example, good recognition results were obtained from the difference of electron transfer resistance (ΔRet), where ΔRetD was larger than ΔRetL and linear responses in ΔRet were found for Lys enantiomers ranging from 100 nM to 10 mM with a detection limit of 33 nM (S/N = 3). In addition, the results of analyzing another four amino acids revealed the specificity of the proposed sensor. The developed sensor with the advantages of simple preparation, long-term stability, good sensitivity and commendable selectivity, holds great potential application for the nanostructured composite adulterated with a chiral selector in chiral bio-electroanalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...