Modifying hydrogen bonding interaction in solvent and dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles: impact on the photovoltaic performance of inverted organic solar cells†
Abstract
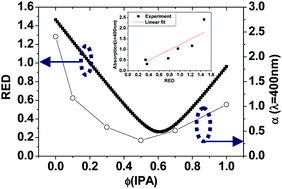
We demonstrate that the morphology of ZnO buffer layers for the inverted organic solar cells (IOSC) was improved by controlling the molecular interaction in solvents to disperse ZnO nanoparticles (NPs). Dispersion of ZnO NPs in non-polar solvent usually resulted in turbid or semi-transparent solution. In this study, uniform dispersion of ZnO NPs was achieved through applying mixed solvents composed of both non-polar and polar solvents without the assistance of an organic surfactant. From the analysis based on Hansen solubility parameter theory, the improvement was mainly associated with hydrogen bonding interactions between the two component of solvents. Smooth ZnO buffer layers were deposited using the colloidal solution based on the binary solvent mixture and the photovoltaic performance of the IOSC was highly improved by optimizing solvent mixtures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...