Radiolytic synthesis of Au–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles supported on TiO2: application in photocatalysis†
Abstract
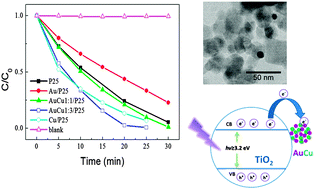
Modification of TiO2 (P25) with Au–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles (NPs) was successfully achieved via a deposition–precipitation method with urea (DPU) followed by radiolytic reduction. This deposition procedure ensures the complete adsorption of Au and Cu ions onto TiO2. Small Au–Cu NPs homogeneous in size were obtained. The alloyed structure of Au–Cu NPs was confirmed by HAADF-STEM, EDS, HRTEM and XPS techniques. The photocatalytic properties of the modified TiO2 have been studied for photodegradation of methyl orange. The modification with Au–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles induces an enhancement in the photocatalytic activity under UV irradiation. The highest photocatalytic activity was obtained with Au–Cu/TiO2 (Au/Cu = 1 : 3). Bimetallic Au–Cu NPs act as efficient electron scavengers increasing the photocatalytic activity under UV light.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...