99mTc-labeled benzothiazole and stilbene derivatives as imaging agents for Aβ plaques in cerebral amyloid angiopathy†
Abstract
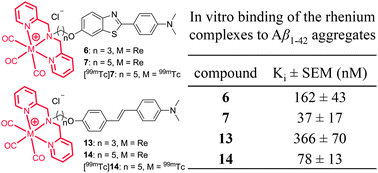
β-Amyloid (Aβ) plaques in the blood vessels of the brain are associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), which is a common cause of stroke and vascular diseases. Imaging agents that can differentiate between Aβ plaques in the brain and those on the walls of cerebrovascular vessels will provide non-invasive biomarkers to interrogate the pathogenesis of CAA and give insights into the mechanisms, significance and impact of Aβ-CAA for developing effective therapies for CAA and stroke. A new series of 99mTc-labeled benzothiazole and stilbene derivatives with positive charge were developed and evaluated for selectively targeting Aβ plaques in the blood vessels of the brain. The rhenium complexes 6, 7, 13 and 14 displayed medium binding affinity to Aβ1–42 aggregates with Ki values of 162, 37, 366 and 78 nM, respectively. In vitro fluorescence staining of 7 and 14 demonstrated an intense labeling of Aβ plaques associated with blood vessel walls on brain sections of a patient with Alzheimer's diseases. A relatively low initial brain uptake for [99mTc]7 and [99mTc]14, 0.18 and 0.24 ID% per gram, respectively, suggests that they may be useful SPECT imaging agents for selectively detecting Aβ plaques associated with cerebral vessels in the living human brain.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...