Synthesis, novel luminescence properties, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering of Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ composite nanotubes
Abstract
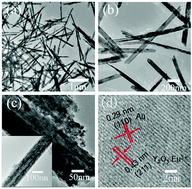
Y(OH)3:Eu3+ nanotubes were synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method first, and then Au particles were grown on the surface of Y2O3:Eu3+ nanotubes by combining the vacuum extraction method and the annealing process. The composite nanotubes were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The effects of the Au content on the photoluminescence properties of the Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ composite nanotubes were investigated in detail. In the excitation spectra of Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ monitored at 614 nm, the 7F0→5H3 transition from Eu3+ increased with increasing Au content, while the other sharp lines originating from Eu3+ f–f electron transitions almost vanished. In the emission spectra, the spectral configurations of Eu3+ in Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ composite nanotubes varied with the excitation wavelengths. When the excitation wavelength was 256 nm, the 5D4→7F0, 5D7→7F0, 5G2→7F0, 5L6→7F0, 5D0→7F0, 5D0→7F1, 5D0→7F2, 5D0→7F3, and 5D0→7F4 transitions from Eu3+ ions in Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ were observed. When the excitation wavelength was 378 nm, the plasmon resonance peak from Au nanoparticles was observed. In addition, 4-ATP was chosen as the model molecule to examine the performance of the Au/Y2O3:Eu3+ composite nanotubes as SERS substrates. The relative intensities of the SERS spectra enhanced with the increase of Au+ : Ln3+ ratio.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...