Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane modified layered double hydroxides greatly facilitate polyoxometalate intercalation†
Abstract
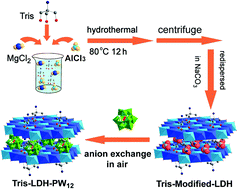
Polyoxometalate (POM) intercalation to layered double hydroxides (LDHs) has been greatly restricted by the geometry, charge and size of POMs. We report herein, for the first time, the intercalation of Na3[PW12O40]·15H2O into tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane (Tris) modified layered double hydroxides (Tris-LDH-CO3) using an ion exchange method, resulting in the formation of novel intercalated Tris-LDH-PW12 under ambient conditions without the necessity of degassing CO2. Theoretical calculations show the decreased energy and the slightly distorted LDH layer after Tris modification, indicating that the Tris-modified LDH layers greatly facilitate the intercalation of PW12. Further application of Tris-LDH-PW12 for oxygenation of sulfides shows highly efficient and selective catalytic activities under mild conditions. The Tris-LDH-PW12 can be easily recovered and reused for more than 10 times without any obvious decrease of reactivity. This opens a completely new pathway for engineering POM-LDH advanced functional materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...