A red phosphor BaTiF6:Mn4+: reaction mechanism, microstructures, optical properties, and applications for white LEDs†
Abstract
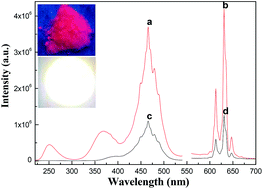
Red phosphors BaTiF6:Mn4+ with microrod and polyhedron morphologies have been prepared respectively by etching TiO2 and Ti(OC4H9)4 in a HF solution with an optimized concentration of KMnO4 at 1.5 mmol L−1 in hydrothermal conditions. The red phosphor BaTiF6:Mn4+ exhibits a broad excitation band in the blue region and sharp emission peaks in the red region. A white LED (WLED) fabricated with the red phosphor BaTiF6:Mn4+ shows “warm” white light that possesses a color rendering index of 93.13 at a color temperature of 4073.1 K.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...