Synthesis, characterization and reactivity studies of electrophilic ruthenium(ii) complexes: a study of H2 activation and labilization†
Abstract
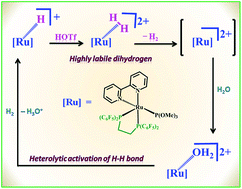
Reaction of 2,2′-bipyridine (bpy) with dinuclear complexes [RuCl(dfppe)(μ-Cl)3Ru(dmso-S)3] (dfppe = 1,2-bis(dipentafluorophenyl phosphino)ethane (C6F5)2PCH2CH2P(C6F5)2; dmso = dimethyl sulfoxide) (1) or [RuCl(dfppe)(μ-Cl)3RuCl(dfppe)] (2) affords the mononuclear species trans-[RuCl2(bpy)(dfppe)] (3). Using this precursor complex (3), a series of new cationic Ru(II) electrophilic complexes [RuCl(L)(bpy)(dfppe)][Z] (L = P(OMe)3 (5), PMe3 (6), CH3CN (7), CO (8), H2O (9); Z = OTf (5, 6, 7, 8), BArF4 (9) have been synthesized via abstraction of chloride by AgOTf or NaBArF4 in the presence of L. Complexes 5 and 6 were converted into the corresponding isomeric hydride derivatives [RuH(PMe3)(bpy)(dfppe)][OTf] (10a, 10b) and [RuH(P(OMe)3)(bpy)(dfppe)][OTf] (11a, 11b) respectively, when treated with NaBH4. Protonation of the cationic monohydride complex (11a) with HOTf at low temperatures resulted in H2 evolution accompanied by the formation of either solvent or triflate bound six coordinated species [Ru(S)(P(OMe)3)(bpy)(dfppe)][OTf]n [(S = solvent (n = 2), triflate (n = 1)] (13a/13b); these species have not been isolated and could not be established with certainty. They (13a/13b) were not isolated, instead the six-coordinated isomeric aqua complexes cis-[Ru(bpy)(dfppe)(OH2)(P(OMe)3)][OTf]2 (14a/14b) were isolated. Reaction of the aqua complexes (14a/14b) with 1 atm of H2 at room temperature in acetone-d6 solvent resulted in heterolytic cleavage of the H–H bond. Results of the studies on H2 lability and heterolytic activation using these complexes are discussed. The complexes 3, 5, 11a, and 14a have been structurally characterized.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...