Calcium phosphate nanoparticles: a study of their synthesis, characterization and mode of interaction with salmon testis DNA
Abstract
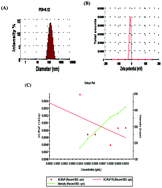
Calcium phosphate nanoparticles (CPNPs) are presently emerging as a second generation vector for efficient delivery and stabilization of nucleic acids inside cells, although the detailed mode of interaction between CPNPs and DNA is still obscure. This study discloses some features of the interaction. For this study, we synthesized CPNPs by a modified co-precipitation method and characterized the particles by different techniques such as dynamic light scattering, X-ray diffraction, electron dispersive spectroscopy, Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy, differential thermal and thermo-gravimetric analysis, and atomic force, scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The characterization studies showed that the nanoparticles were spherical in shape, about 45 nm in size and were composed of the hydroxyapatite form of calcium phosphate; almost 90% of the starting materials were converted to nanoparticles (NPs). The different aspects of the interaction between CPNPs and salmon testis DNA were investigated using techniques such as UV-Vis spectrophotometry, circular dichroism, Fourier transform infra-red spectrometry, thermal denaturation, microviscometry, agarose gel electrophoresis, cyclic voltammetry and atomic force microscopy. The results revealed that CPNPs interacted with DNA with ∼1 : 3.3 stoichiometry with a binding constant of the order of 104 M−1 through groove-interacting mode and a single nanoparticle covered about 6.2 base pairs of the DNA chain. Moreover, the binding interaction was spontaneous, cooperative, exothermic and enthalpy-driven and some electrostatic nature of the binding was also evident; however, the non-polyelectrolyte contribution was dominant. The binding interaction finally caused an increase in the melting temperature of DNA from 70.8 °C to 75 °C and alteration of its secondary structure from the naturally occurring B-form to C-form.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...