A floating macro/mesoporous crystalline anatase TiO2 ceramic with enhanced photocatalytic performance for recalcitrant wastewater degradation†
Abstract
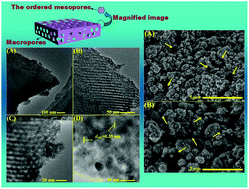
A macro/mesoporous anatase TiO2 ceramic floating photocatalyst has been successfully synthesized using highly thermally stable mesoporous TiO2 powder as a precursor, followed by a camphene-based freeze-casting process and high-temperature calcinations. The ceramics are characterized in detail by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectra, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms. The results indicate that the TiO2 ceramics present hierarchical macro/mesoporous structures, which maintain high porosity and high compressive strength at the optimal sintering temperature of 800 °C. The ordered mesoporous TiO2 network still possesses high thermal stability and inhibits the anatase-to-rutile phase transformation during calcinations. The obtained ceramics exhibit good adsorptive and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of octane and rhodamine B, and the total organic carbon removal ratio is up to 98.8% and 98.6% after photodegradation for 3 h, respectively. The roles of active species in the photocatalytic process are compared using different types of active species scavengers, and the degradation mechanism is also proposed. Furthermore, the ceramics are recyclable, and no clear changes are observed after ten cycles. In addition, the ceramics are also active in the photodegradation of phenol, thiobencarb, and atrazine. Therefore, these novel floating photocatalysts will have wide applications, including the removal of floating organic pollutants from the wastewater surfaces or the removal of soluble organic pollutants from wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...