Finding needles in a basestack: recognition of mismatched base pairs in DNA by small molecules
Abstract
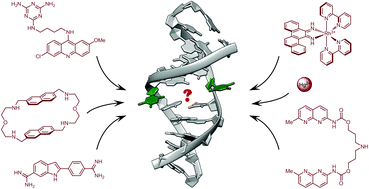
Mismatched (non-Watson–Crick) base pairs represent the most common type of DNA damage, as they are permanently formed in living cells due to erroneous insertion, deletion and misincorporation of bases. In vivo, they are readily recognised and repaired by the proteins of the DNA mismatch repair system, which identify the mismatch sites with high efficiency and fidelity. Notably, the last decades have witnessed the development of several chemically diverse families of small organic molecules and metal complexes that selectively bind to mismatched base pairs (and not to fully paired double-stranded DNA), much like the proteins of the mismatch repair system. This review focuses on these DNA mismatch-binding ligands, with an emphasis on their (often unusual) binding modes, as well as on the similarities and differences between the different classes of mismatch binders. Also discussed are the potential bioanalytical and therapeutic applications of mismatch-binding ligands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...