A fullerene–carbene adduct as a crystalline molecular rotor: remarkable behavior of a spherically-shaped rotator†
Abstract
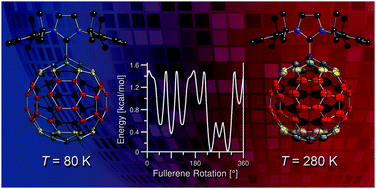
A new fullerene structure was recently obtained from the reaction of a Lewis basic N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) and the Lewis acidic C60. The molecular features of the zwitterionic adduct can be described as a molecular rotor with the fullerene cage acting as the rotator that spins about one distinct axis given by its C–C single bond linkage with the imidazolium heterocycle stator. A detailed structural analysis of the compound by means of single-crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed significant differences in the packing motifs of solvent-free and solvent-containing crystals. Variable temperature single-crystal XRD experiments (80 K ≤ T ≤ 480 K) carried out to investigate the rotational dynamics of the fullerene group in the higher quality solvent-free structure revealed atomic displacement parameters consistent with fast rotation of the highly symmetric fullerene in the solid state, whereas the imidazolium unit remains in a fixed position and therefore represents the stator. DFT and semiempirical calculations were applied to get insight into the profile of the rotational potential of the fullerene unit, particularly considering interactions with the neighboring molecules in the crystal lattice. The results indicate that the crystal environment leads to the presence of one lowest energy minimum that is connected to seven others that are slightly higher in energy through rotational barriers of approximately 1.5–2.5 kcal mol−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...