A family of three magnetic metal organic frameworks: their synthesis, structural, magnetic and vapour adsorption study†‡
Abstract
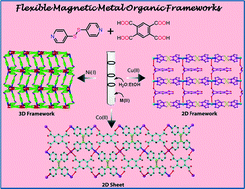
Three flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based on aldrithiol linker and pyromellitate ligand, namely, [Co(aldrithiol)(pyromellitate)0.5(H2O)2]n (1), [Ni2(aldrithiol)2(pyromellitate)(H2O)2]n·2n(C2H5OH)·11n(H2O) (2) and [Cu(aldrithiol)2(pyromellitate)]n·2n(H2O) (3) have been synthesized through slow diffusion technique and characterized by structural, magnetic and adsorption studies. Single crystal X-ray studies show that compounds 1 and 3 have two-dimensional layered structures, whereas compound 2 adopts a three-dimensional framework structure. The observed dimensionality change might be due to the different orientation of pyridine rings in the flexible aldrithiol linker and versatile bridging modes of the pyromellitate ligand. In 1 and 2, the pyromellitate ligand coordinates to the metal centre in a monodentate fashion {(κ1)-(κ1)-(κ1)-(κ1)-μ4} and in 3, it coordinates in {(κ1)-(κ1)-μ2} fashion. The magnetic properties of 1–3 were investigated in detail and show weak antiferromagnetic coupling among the metal centres. Vapour sorption studies reveal that compounds 1 and 3 show high methanol vapour uptake, whereas compound 2 shows a decent amount of H2O adsorption. The dehydrated frameworks of 1–3 regenerate the as-synthesized framework structures upon exposure to water vapour.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of Crystallography Celebration: India

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...