Amplified binding-induced homogeneous assay through catalytic cycling of analyte for ultrasensitive protein detection†
Abstract
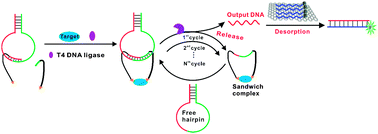
By using the principle of binding-induced DNA assembly, we have developed a novel homogeneous assay that is able to convert an affinity protein binding event into a predesigned DNA assembly. The assembled DNA sequence can be ligated into an intact DNA strand and hundreds of DNA hairpins can be cleaved by a nicking endonuclease. Each cleavage releases a single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) probe that is initially caged in the DNA hairpin. This released ssDNA probe can then turn on the fluorescence signal by desorbing a fluorescently-labelled complementary DNA probe from graphene oxide through hybridization. We demonstrate that this homogeneous, isothermal, and amplifiable assay can be tailored to detect a number of proteins, including a cancer biomarker, human prostate specific antigen, at picomolar levels in both buffer and human serum samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...