An anthraquinone moiety/cysteamine functionalized-gold nanoparticle/chitosan based nanostructured composite for the electroanalytical detection of dissolved oxygen within aqueous media†
Abstract
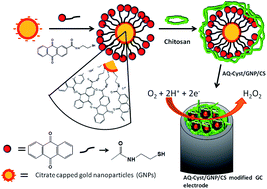
This work reports a nanostructured composite electrode comprising gold nanoparticles, anthraquinone derivatives and chitosan electrically wired via immobilisation upon a glassy carbon macroelectrode. The as-prepared nanostructured composite was morphologically characterised using transmission electron microscopy with surface characterization performed with atomic force microscopy while other physical characterization was undertaken by infra-red, UV-Vis, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Electrochemical investigations and stability measurements of the composite electrode were performed by cyclic voltammetry. Electrocatalytic activity of the composite electrode was investigated for the oxygen reduction reaction in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution of pH 6.5. Furthermore, the response characteristics show that this fabricated electrode has a shelf-life of between 3 and 4 months and has improved electrochemical and electrical properties and firm adhesion of the material with homogeneous dispersion at the electrode surface. The linear range and detection limit for the electrochemical detection of dissolved oxygen under the optimum conditions using the nanostructured composite was found to be over the accessible range of 0.2 to 5.8 mg L−1 and 0.03 mg L−1 respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...