LOC-SERS: towards point-of-care diagnostic of methotrexate
Abstract
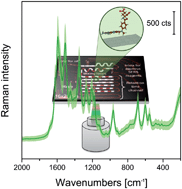
Therapeutic drug monitoring is of major importance in the case of medication with a narrow therapeutic range as well as when pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic variability is suspected. Methotrexate (MTX), an antifolate antibiotic, proved to be toxic regardless of the chosen treatment schedule. In this contribution, a new analytical method was used for the detection of MTX. A linear response was achieved in the 0.2–2 μM concentration range, with a limit of detection ≈ 0.17 μM. The lab-on-a-chip surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (LOC-SERS) approach combines the fingerprint specificity and high sensitivity of SERS with the high sample throughput of a microfluidic platform. Additionally, it is shown that due to the chemical affinity of the MTX molecules towards Ag nanostructures, the pH value of the solving medium highly affects the obtained SERS signal. More specifically, SERS signals with well resolved bands can be obtained from deprotonated MTX molecules due to their binding to the metallic surface via the amine groups of the aromatic ring.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Clinical Diagnostics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...