Hyperspectral reflected light microscopy of plasmonic Au/Ag alloy nanoparticles incubated as multiplex chromatic biomarkers with cancer cells
Abstract
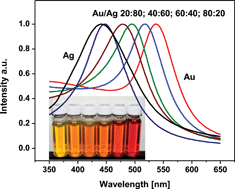
A hyperspectral microscopy system based on a reflected light method for plasmonic nanoparticle (NP) imaging was designed and compared with a conventional darkfield method for spatial localization and spectroscopic identification of single Au, Ag and Au/Ag alloy NPs incubated with fixed human cancer cell preparations. A new synthesis protocol based on co-reduction of Au and Ag salts combined with the seeded growth technique was used for the fabrication of monodispersed alloy NPs with sizes ranging from 30 to 100 nm in diameter. We validated theoretically and experimentally the performance of 60 nm Au, Ag and Au/Ag (50 : 50) NPs as multiplexed biological chromatic markers for biomedical diagnostics and optical biosensing. The advantages of the proposed reflected light microscopy method are presented for NP imaging in a complex and highly diffusing medium such as a cellular environment. The obtained information is essential for the development of a high throughput, selective and efficient strategy for cancer detection and treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...