Highly dispersed Au nanoparticles immobilized on Zr-based metal–organic frameworks as heterostructured catalyst for CO oxidation†
Abstract
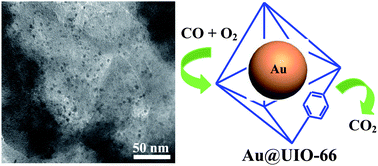
Highly dispersed Au nanoparticles have been immobilized on the Zr(IV)-based metal–organic framework UIO-66 via a simple one-step chemical wetting method, in which oleylamine used as both a reducing and a stabilizing agent with HAuCl4 as the gold precursor is introduced to embed Au nanoparticles into the framework. The resulting Au@UIO-66 catalyst is characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, N2 physical adsorption, and transmission electron microscopy. It is found that most of the Au nanoparticles with sizes of 1–3 nm are evenly distributed over the UIO-66 matrix. The Au@UIO-66 heterostructures exhibit high catalytic activity and stability for gas-phase CO oxidation. The observed high activity is mainly attributed to the small size of Au nanoparticles and their high dispersion within the pores of UIO-66.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...