Compact tridentate ligands for enhanced aqueous stability of quantum dots and in vivo imaging†
Abstract
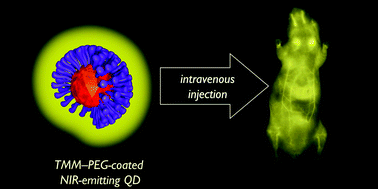
We describe here a simple and versatile route for the preparation of a tridentate
* Corresponding authors
a
CEA, iBiTecS, Service de Chimie Bioorganique et de Marquage, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
E-mail:
eric.doris@cea.fr
Fax: +33 169 08 79 91
Tel: +33 169 08 80 71
b
Laboratoire de Physique et d'Etude des Matériaux, UMR8213 du CNRS, ESPCI, 10 rue Vauquelin, 75005 Paris, France
E-mail:
benoit.dubertret@espci.fr
Tel: +33 140 79 45 92
c CEA, I2BM, Service Hospitalier Frédéric Joliot, INSERM U1023, Laboratoire d'Imagerie Moléculaire Expérimentale, Université Paris Sud, 4 place du général Leclerc, 91401 Orsay, France
We describe here a simple and versatile route for the preparation of a tridentate

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
E. Gravel, C. Tanguy, E. Cassette, T. Pons, F. Knittel, N. Bernards, A. Garofalakis, F. Ducongé, B. Dubertret and E. Doris, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 411 DOI: 10.1039/C2SC21113K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
