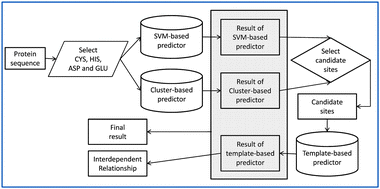
As one of the most important trace elements within an organism, zinc has been shown to be involved in numerous biological processes and closely implicated in various diseases. The zinc ion is important for proteins to perform their functional roles. To provide in-depth functional annotation of zinc-binding proteins, an initial but crucial step is the accurate recognition of zinc-binding sites. Motivated by the biological importance of zinc, we propose a new method called ZincExplorer to predict zinc-binding sites from protein sequences. ZincExplorer is a hybrid method that can accurately predict zinc-binding sites from protein sequences. It integrates the outputs of three different types of predictors, namely, SVM-, cluster- and template-based predictors. Four types of zinc-binding amino acids CHEDs (i.e. CYS, HIS, ASP and GLU) could be predicted using ZincExplorer. It achieved a high AURPC (Area Under Recall–Precision Curve) of 0.851, and a precision of 85.6% (specificity = 98.4%, MCC = 0.747) at the 70.0% recall for the CHEDs on the 5-fold cross-validation test. When tested on an independent dataset containing 2023 zinc-binding CHEDs and 14 493 non-zinc-binding CHEDs, it achieved about 3–8% higher AURPC in comparison to two other sequence-based predictors. Moreover, ZincExplorer could also identify the interdependent relationships (IRs) of the predicted zinc-binding sites bound to the same zinc ion, which makes it a useful tool for providing in-depth zinc-binding site annotation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...