Furan: a critical heat induced dietary contaminant
Abstract
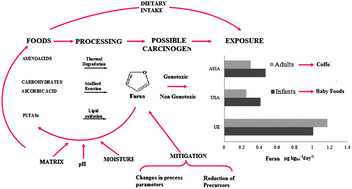
The presence of
- This article is part of the themed collection: The Maillard reaction in food and nutrition
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Chemical Engineering and Bioprocess, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Av. Vicuña Mackenna 4860, Santiago, Chile
E-mail:
msmariot@uc.cl
Fax: +56-2-3547962
Tel: +56-2-3541269
b National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark, Mørkhøj Bygade 19, Søborg, Copenhagen, Denmark
c Department of Nutrition, Diabetes and Metabolism, School of Medicine, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Lira 40, Santiago, Chile
d ASIS-UC Interdisciplinary Research Program on Tasty and Healthy Foods, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Casilla 306, Correo 22, Santiago, Chile
The presence of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. S. Mariotti, K. Granby, J. Rozowski and F. Pedreschi, Food Funct., 2013, 4, 1001 DOI: 10.1039/C3FO30375F
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
