Platinum(ii) and platinum(iv) complexes stabilized by abnormal/mesoionic C4-bound dicarbenes†
Abstract
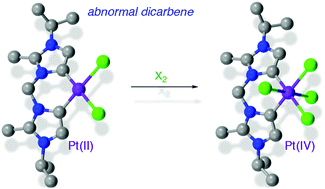
Platinum(II) complexes comprising abnormal diimidazolylidene
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanistic Organometallic Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...