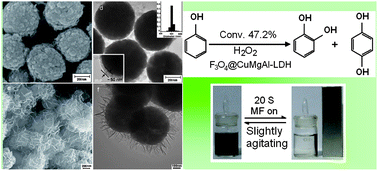
Novel hierarchical core@shell structured magnetic nanocatalysts of various morphologies involving ternary Cu-based layered double hydroxide CuMgAl-LDH shells and Fe3O4 cores were prepared via one-pot coprecipitation assembly and systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning/transmission electron microscopy (SEM/TEM)/high-resolution (HR) TEM, vibrating-sample magnetometry (VSM), H2-temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The nanocatalyst Fe3O4@CuMgAl-1 is revealed as a ca. 50 nm thick CuMgAl-LDH nanoshell consisting of 20 nm plate-like LDH particles horizontally coated onto the surface of the Fe3O4 core (ca. 500 nm in diameter), while Fe3O4@CuMgAl-2 shows honeycomb-like morphology with ca. 200 nm hexagonal plate-like LDH particles vertically grown on the surface of the Fe3O4 core. Both magnetic nanocatalysts exhibit higher catalytic activity for phenol hydroxylation by H2O2 than pure CuMgAl-LDH, and the former is better than the latter. These results can be rationally explained by a hydroxyl radical mechanism, resulting from Cu2+/Fe2+ and H2O2via a Fenton-like reagent, enhanced by the synergetic effect between the CuMgAl-LDH shell and the Fe3O4 core, possibly via a Cu–O–Fe linkage. In addition, the as-prepared magnetic nanocatalysts possess strong magnetic properties and a high magnetic reuse efficiency.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...