Charge transfer properties of a donor–acceptor dyad based on an expanded acridinium cation†
Abstract
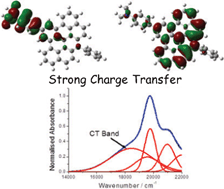
Photophysical properties of a donor–acceptor dyad are discussed, which is based on an N,N-dimethylaniline subunit connected to an expanded acridinium

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...