Photoelectrochemical cells for solar hydrogen production: current state of promising photoelectrodes, methods to improve their properties, and outlook
Abstract
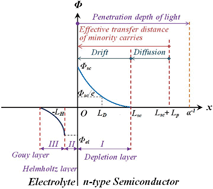
Harnessing solar energy for the production of clean hydrogen fuels by a photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell represents a very attractive but challenging alternative. This review focuses on recent developments of some promising photoelectrode materials, such as BiVO4, a-Fe2O3, TaON, and Ta3N5 for solar hydrogen production. Some strategies have been developed to improve PEC performances of the photoelectrode materials, including: (i) doping for enhancing visible light absorption in the wide bandgap semiconductor or promoting charge transport in the narrow bandgap semiconductor, respectively; (ii) surface treatment for removing segregation phase or surface states; (iii) electrocatalysts for decreasing the overpotentials; (iv) morphology control for enhancing the light absorption and shortening transfer distance of minority carriers; (v) other methods, such as sensitization, passivating layer, and band structure engineering using heterojunction structures, and so on. Photochemical durability of the photoelectrodes is also discussed, since any potential PEC technology must balance efficiency against cost and photochemical durability. Photochemical durability may be amended by optimizing the photoelectrode, electrocatalyst, and electrolyte at the same time. In addition, solar seawater splitting is briefly introduced because it has received attention recently. Finally, trends in research in PEC cells for solar hydrogen production are detailed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...