Oxygen reduction at sparse arrays of platinum nanoparticles in aqueous acid: hydrogen peroxide as a liberated two electron intermediate
Abstract
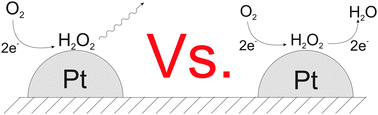
Electrodeposition methods are used to generate a sparse array of platinum nanoparticles on a glassy carbon electrode. Specifically electrodeposition from a 1 mM solution of H2PtCl6 in 0.5 M H2SO4 leads to surface coverages of 0.46% to 1.96% and nanoparticles of size 29 nm to 136 nm in diameter, using deposition times of 30 and 15 seconds. The reduction of oxygen at an array of 29 nm nanoparticles with a surface coverage of 0.46% showed voltammetric signals with a scan rate dependence consistent with a two electron reduction of O2 to H2O2 with the rate proportional to 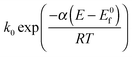 and formal potential (E0f) of −0.058 V vs. SHE, a standard electrochemical rate constant (k0) of ∼10 cm s−1 and a transfer coefficient (α) of 0.23. At higher Pt nanoparticle coverages, a scan rate dependence consistent with the partial further reduction of H2O2 to water becomes evident.
and formal potential (E0f) of −0.058 V vs. SHE, a standard electrochemical rate constant (k0) of ∼10 cm s−1 and a transfer coefficient (α) of 0.23. At higher Pt nanoparticle coverages, a scan rate dependence consistent with the partial further reduction of H2O2 to water becomes evident.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...