Study of aqueous phase aggregation of FTY720 (fingolimod hydrochloride) and its effect on DMPC liposomes using fluorescent molecular probes†
Abstract
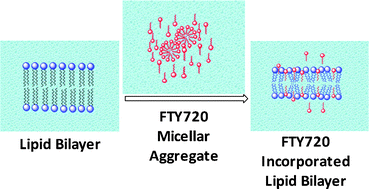
This work focuses on the study of aqueous phase aggregation of the recently FDA approved oral drug molecule FTY720 (fingolimod hydrochloride) and its effect on dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) liposomes using different fluorescent molecular probes and fluorescence parameters. The variation of the steady state fluorescence intensity of 8-anilino-1-naphthalene sulfonic acid (ANS) with FTY720 in water shows an efficient micellar aggregation with the critical micellar concentration (CMC) at ∼75 μM. The aggregation number calculation from steady state fluorescence quenching of pyrene shows the formation of small micellar aggregates in aqueous solution having an aggregation number of 42 ± 3 with the free energy of micellization ∼−23 kJ mol−1. Fluorescence intensity and lifetime decay analysis of the molecular probe 1-naphthol indicate that the interaction of FTY720 with the DMPC lipid bilayer membrane prevents partitioning of small molecules such as 1-naphthol to the membrane in both solid gel (SG) and liquid crystalline (LC) phases. Temperature dependent fluorescence intensity studies of 1-naphthol and fluorescence anisotropy measurements of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene (DPH) have shown that above the CMC of FTY720, the SG to LC main phase transition temperature (TM) of the lipid bilayer membrane decreases from 23 °C to 21 °C in the aqueous medium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...