Synthesis and pH-responsive micellization of brush copolymers poly(methyl methacrylate-co-2-(2-bromoisobutyryloxy)ethyl methacrylate-graft-acrylic acid): role of composition profile
Abstract
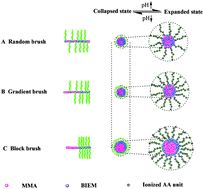
A series of brush copolymers (i.e. poly(methyl methacrylate (MMA)-co-2-(2-bromoisobutyryloxy)ethyl methacrylate (BIEM)-graft-acrylic acid (AA))) having three backbone composition profiles, i.e. random, gradient and block, were synthesized via the combination of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP)/model-based semibatch ATRcoP and the “grafting from” method. These samples allowed us to systematically investigate the effects of the composition profile (including the grafting density corresponding to the composition profile) on the micelle formation and pH responsivity of the brush copolymers in solution. FTIR, 1H NMR and GPC were used to provide evidence for the formation of the well-defined brush copolymers. TEM, light transmittance and DLS were used to investigate the self-assembly and pH responsivity of the resulting copolymers. It was found that the micelles formed by these copolymers underwent a different conformational transition caused by the change from acidic to basic in the solution. These transitions were mainly influenced by pH and composition profile since the composition profile also had a strong effect on the acid-dissociation degree of the brush copolymer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...