Silver oxide particles/silver nanoparticles interconversion: susceptibility of forward/backward reactions to the chemical environment at room temperature†
Abstract
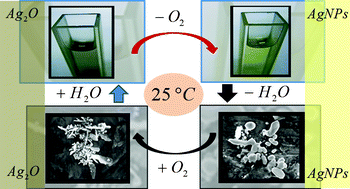
The thermal stability of the silver oxide particles (Ag2O)/metallic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) system in aqueous and gaseous environments is investigated with UV-Visible spectroscopy, TEM, SEM and DLS as characterisation techniques, and with calculations using electromagnetic theory. Thermal decomposition of aqueous Ag2O colloids to produce AgNPs is conclusively demonstrated and used as a base reaction to produce clean AgNPs without any external reducing agent. Such a spontaneous character of Ag2O decomposition in alkaline aqueous/water-enriched environments at room temperature makes the formation of silver oxide films on silver nanoparticles/nanostructures unlikely, keeping the silver surface oxide-free, a crucial feature in determining the silver catalytic and Raman enhancing properties. The synthetic suitability of this reaction to develop new routes to produce AgNPs is explored by analyzing the effect of temperature, complexing agents, and environment polarity on the AgNPs size/shape control. Thermal decomposition of Ag2O colloids in aqueous/water-enriched environments offers the possibility to produce AgNPs at low cost, with easy, clean, safe and green chemistry procedures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...