Abstract
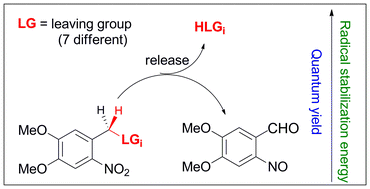
Quantum yields for the photoinduced release of seven different commonly used leaving groups (LGs) from the o-nitroveratryl protecting group were measured. It was found that these quantum yields depend strongly on the nature of the LGs. We show that the quantum efficiency with which the LGs are released correlates with the stabilization that these LGs provide to o-nitrobenzyl-type radicals because radical stabilizing groups weaken the C–H bond that is cleaved in the photoinduced hydrogen atom transfer step, and hence lower the barrier for this process. At the same time these substituents lower the endothermicity of the thermal hydrogen atom transfer and thus increase the barrier for the reverse process, thereby enhancing the part of the initially formed aci-nitro intermediates which undergo
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photoremovable protecting groups: development and applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...