Controlling the initial growth behavior of SrTiO3 films by interposing Al2O3 layers between the film and the Ru substrate
Abstract
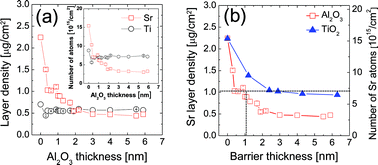
The effects of thin Al2O3 layers interposed between atomic layer deposited SrTiO3 (STO) films and Ru substrates on the growth and properties of STO films were examined. Although a 3–4 nm thick TiO2 barrier layer was necessary to completely suppress the oxygen diffusion from the underlying Ru(O) layer, which could result in uncontrolled excessive Sr incorporation into the film, a 2–3 nm thick Al2O3 barrier layer was sufficient to achieve the saturated oxygen blocking effect. Therefore, only a 0.4 nm thick Al2O3 layer could effectively suppress uncontrollable initial excessive incorporation of Sr, and a 1 nm thick Al2O3 layer had a blocking effect that was equivalent to that of a 3 nm thick TiO2 layer. STO films were crystallized in situ by the assistance of crystallized 2–3 nm thick STO seed layers that were pre-deposited and annealed. The bulk dielectric constant of STO calculated by the slope of equivalent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...