Nitrogen doping of graphene and its effect on quantum capacitance, and a new insight on the enhanced capacitance of N-doped carbon†
Abstract
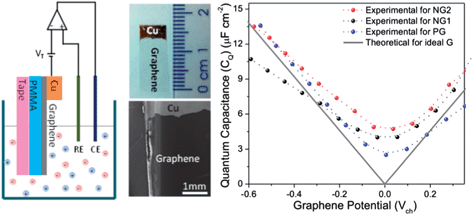
Many researchers have used nitrogen (N) as a dopant and/or N-containing functional groups to enhance the capacitance of carbon electrodes of electrical double layer (EDL) capacitors. However, the physical mechanism(s) giving rise to the interfacial capacitance of the N-containing carbon electrodes is not well understood. Here, we show that the area-normalized capacitance of lightly N-doped activated graphene with similar porous structure increased from 6 μF cm−2 to 22 μF cm−2 with 0 at%, and 2.3 at% N-doping, respectively. The quantum capacitance of pristine single layer graphene and various N-doped graphene was measured and a trend of upwards shifts of the Dirac Point with increasing N concentration was observed. The increase in bulk capacitance with increasing N concentration, and the increase of the quantum capacitance in the N-doped monolayer graphene versus pristine monolayer graphene suggests that the increase in the EDL type of capacitance of many, if not all, N-doped carbon electrodes studied to date, is primarily due to the modification of the electronic structure of the graphene by the N dopant. It was further found that the quantum capacitance is closely related to the N dopant concentration and N-doping provides an effective way to increase the density of the states of monolayer graphene.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...