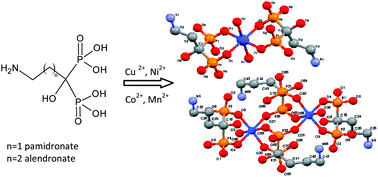
In the search for a pharmacological answer to treat Chagas disease, eight metal complexes with two bioactive bisphosphonates, alendronate (Ale) and pamidronate (Pam), were described. Complexes of the formula [M2II(Ale)4(H2O)2]·2H2O, with M = Cu, Co, Mn, Ni, and ([CuPam]·H2O)n as well as [MII(Pam)2(H2O)2]·3H2O, with M = Co, Mn and Ni, were synthesized and fully characterized. Crystal structure of [Cu2II(Ale)4(H2O)2]·2H2O, [CoII(Pam)2(H2O)2] and [NiII(Pam)2(H2O)2] were solved by X-ray single crystal diffraction methods and the structures of [M2II(Ale)4(H2O)2]·2H2O complexes M = Co, Mn and Ni were studied by X-ray powder diffraction methods. All obtained complexes were active against the amastigote form of Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), etiological agent of Chagas disease. Most of them were more active than the corresponding free ligands showing no toxicity for mammalian cells. The main mechanism of the antiparasitic action of bisphosphonates, inhibition of parasitic farnesyl diphosphate synthase (TcFPPS), remains in the obtained metal complexes and an increase in the inhibiting enzyme levels was observed upon coordination. Observed enzymatic inhibition was selective for TcFPPS as the metal complexes showed no or little inhibition of human FPPS. Additionally, metal complexation might improve the bioavailability of the complexes through the hindrance of the phosphonate group's ionization at physiological pH and, eventually, through the ability of plasma proteins to work as complex transporters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...