Inhibition of peroxynitrite- and peroxidase-mediated proteintyrosine nitration by imidazole-based thiourea and selenourea derivatives†
Abstract
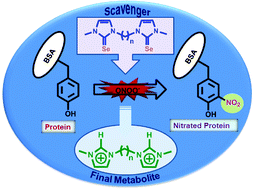
In the present study, the synthesis and characterization of a series of N-methylimidazole-based ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S bonds in
S bonds in ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Se bonds in the corresponding selenoureas. Therefore, the selenium compounds can react with PN or
Se bonds in the corresponding selenoureas. Therefore, the selenium compounds can react with PN or

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...